The GSM-AT protocol is used when you want to communicate with a cellular modem by COM port, whether physical or virtual.
Cellular hardware is the single most reliable and efficient method of delivering SMS. By using cellular hardware, you're removing PageGate's reliance on your internet connection to deliver your messages which means that your internet connection could go down and your messages would still be delivered. It's also incredibly important to note that allowing PageGate to interact with cellular hardware is the only method of configuring a two-way messaging system with SMS.
The basic device, a cellular modem, connects to the system PageGate is installed on by USB or RS232 and provides a COM port in the operating system. If PageGate is running in a virtual environment, you can also connect a cellular modem to a COM port virtualizer that provides the COM port to the virtual machine. This grants PageGate access to the cellular modem, which allows it to send and receive text messages just like a cell phone does. A good example of a cellular modem is Multitech's MTC-H5 series. It's also important to note that there are COM port virtualizers that will allow you to access a cellular modem from a virtual server. So, if you have PageGate installed in a virtual environment, it's still entirely possible to use cellular modems.
It's also possible to turn an Android phone in to a cellular modem with NotePage's new Android SMS Gateway App. When the smart phone is connected by wifi to the same network as the PageGate server, this app grants PageGate access to the smart phone and allows PageGate to use that cell phone to send and receive text messages. It is important to note that all carrier rules regarding sending text messages for the cell phone plan on the phone apply. To configure a carrier to use an Android SMS Gateway phone, you'll need to create a GSM-AT-IP carrier.
1)Right click Carriers.
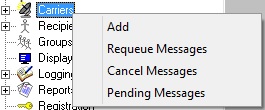
2)Select Add.
3)Select the GSM-AT protocol.
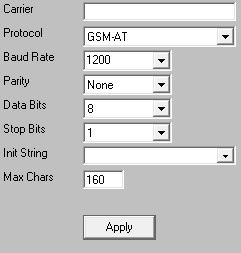
4)Enter a name in the Carrier field.
5)Set the Baud Rate, Parity, Data Bits and Stop Bits to match the device's requirements.
By default, most cellular modems use the following parameters:
Baud Rate: 115200
Parity: None
Data Bits: 8
Stop Bits: 1
6)The Init String field optional for a GSM-AT carrier. To have the program perform a signal quality check on the cellular modem before each delivery, click inside the Init String field and type the following: AT+CSQ
7)Set the Max Chars to: 160
Note: The Carrier Max Chars field determines the number of characters that can be received in a single message. If the recipient Max Chars value is set higher than the carrier Max Chars value, PageGate will break up long messages based on the character limitation in the carrier. For example, if you have the carrier configured for 160 Max Chars and you set the recipient Max Chars value to 3000, then send a 400 character message to this recipient, PageGate will break up the 400 character count message in to two 160 character messages and one 80 character message. When the device receives the message, it will be prefixed with part 1/3, 2/3, 3/3 to indicate the multi-part nature of the message delivered.
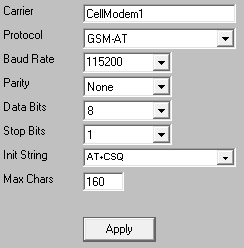
8)Click Apply.
9)Go to Connectors - Connector X - Settings.
Note: Any connector can use a cellular modem but a connector can only be tied to one cellular modem at a time. Multiple connectors cannot reference the same cellular modem.
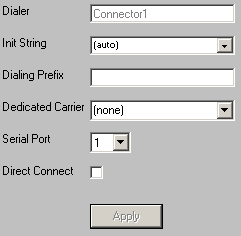
10) Set the Serial Port field to match the COM port of your modem.
11) Click Apply.
When configuring PageGate to use a cellular router or gateway, each manufacturer uses a slightly different command set to perform the same tasks and there are certain Settings template variables that you can apply to GSM-AT-IP carriers to decrease the amount of time it takes to negotiate connections with your hardware.
To implement a two-way messaging system, please see the Two Way Messaging section of the documentation.
Click here for a list of Settings Variables that can be used with GSM-AT Carriers